Table of Contents
Unit 1 | Algebra
Page 1 | Expressions and Formulae
Page 3| Solving Linear Equations
Page 4| Expanding and Factorising
Page 5| Factorising Quadratics and expanding double brackets
Page 6| Patterns and Sequences
Page 7| Simultaneous Equations
Page 8| Changing the subject of a Formula
Page 9| Adding , subtracting algebraic formulas
Unit 2 |Graphs
Page 1 | Straight line graphs
Page 2 | Graphs of Quadratic functions
Unit 3 |Geometry and Measure
Page 2 | Symmetry
Page 3 | Coordinates
Page 4 | Perimeter, Area, Volume
Page 6 | Measurement
Page 7 | Trigonometry
Page 8 | Pythagoras
Page 9 | Angles
Page 10 | Shapes
Page 11| Time
Page 12 | Locus
Unit 4 | Numbers
Page 1 | Speed, Distance and time
Page 2 | Rounding and estimating
Page 3 | Ratio and proportion
Page 4 | Factors, Multiples and primes
Page 5 | Powers and roots
Page 7 | Positive and negative numbers
Page 8 | Basic operations
Page 9 | Fractions
Page 10 | Percentages
Unit 5 | Statistics and Probability
Page 1 | Sampling data (MA)
Page 2 | Recording and representing data
Page 3 | Mean median range and mode
Page 4 | Standard deviation
Unit 4 | Calculus
Number Sequences
A sequence is a list of numbers. The next number of the sequence is found using a rule ( eg. +3 , x2 etc) and every sequence has its own rule. The first thing you need to do when you have a question about sequences is find out what the rule is.
Some of the sequences will be really easy to figure out but others might take a little bit of work. One of the things you could do is find out what the difference is between the numbers that you already have and hopefully you should be able to spot what is going on.
Example 1:
This is the sequence
7, 11, 15, 19, …, …
Let’s find out what the differences are.
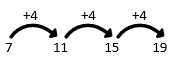
The pattern is clearly adding four so to find the next two numbers all we have to is carry on adding 4
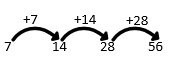
Example 2:
Let’s try another sequence.
7, 14, 28, 56, …, …
Again, we need to find out what the differences are.
Sometimes a sequence will be shown as a pattern that is drawn rather than as numbers. In that case, you just have to do the same thing but first write down the numbers in the pattern that you already have first.
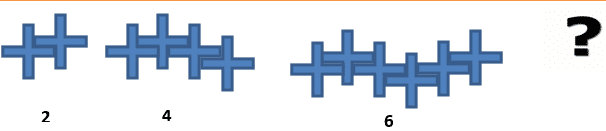
1) Complete the sequence.
![]()
2) Sally makes bracelets of different sizes. She uses pendants![]() and charms
and charms![]() to make the bracelets.
to make the bracelets.
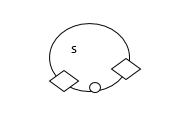
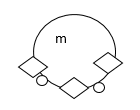
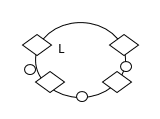
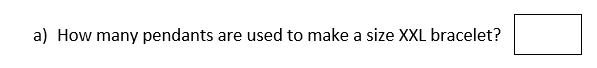
3) The first five multiples of 45 are shown below.
45 90 135 180 215
Boris says; the thirteenth number in the sequence will be 560. What working out the thirteenth number , explain why Boris is wrong.
4) Helen is creating a sequence of number. She starts with the number 2 and creates the next number by squaring it and subtracting 2.
Write down the next four number in the sequence .
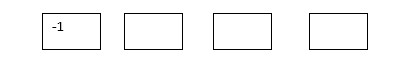
5) Add in the missing number in the sequence. Explain the rule used to find the number.