Nerves and Hormones
L.O To learn about the nervous system and how it works and how hormones can control conditions inside humans and plants.
Nervous system
The human nervous system consists of two parts:
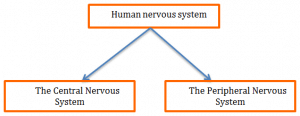
The central nervous system is the main control centers like the brain and the spinal chord.
The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves, which reach the rest of the body which is also known as the periphery.
Nerve cell
Nerve cells can also be called neurons and carry messages known as impulses
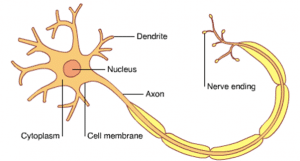
Nerves carry the impulse through the body and then the nerve is sent to the rest of the body through the dendrites which have many other nerves attached to it.
There are two types of neurons sensory and motor neurons.
Sensory neurons are involved in relaying the impulses from the point of impact or otherwise known as the receptors to the central nervous system
The central nervous system then decides what action to take, and it then send another set of impulses through a set of motor neurons to the effector.

Receptors
Receptors are a group of cells, which help to detect a change in the environment for example, your skin will detect if the temperature change around you.
Your skin can also detect pain and it will be send an impulse to the CNS which will then respond to move you body part away from pain.
Your eyes will respond to the light by either dilating or constricting
Effectors
Effectors are parts of the body that respond to what the receptor has felt. This can come in the form of a muscle contracting or a gland releasing a hormone or saliva.
The effector will then stimulate a response.
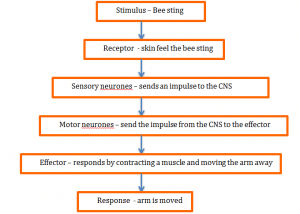
Reflex actions
A reflex action is the way the body quickly reacts to dangerous situations. It follows a sequence which does not involve the brain
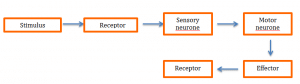
This nerve action is called the reflex arc
The reflex arc process –
- The receptor detects the stimulus
- Sensory neurons send the impulse to the spinal chord
- The spinal chord sends an impulse via the motor neurone
- The effector then responds
The synapse
Where two neurons join together, there is usually a tiny gap called a synapse. the impulse crosses this gap in the for of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These diffuse across the gap and continue the synapse
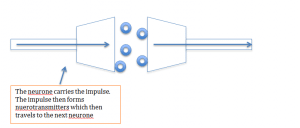
Hormones
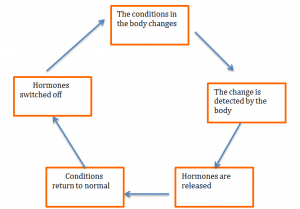
The conditions in our body are carefully controlled by hormones, to ensure that everything is constant and our body functions efficiently.
There are several aspects of our body that need to be controlled. Body temperature needs to be controlled to ensure that the enzymes can work efficiently
Blood sugar levels need to be controlled to ensure the brain has the correct levels of glucose
Water content also needs to controlled to ensure our cells have the correct amount of water. Too much water can cause cells to burst and too little will cause cells to shrink.
Hormones use a system called negative feedback, which allows them to maintain the conditions at just the right level.
One of the main hormones in the body is insulin. Glucose levels are regulated in the body by insulin which ensures that the levels do not get too high or too low. Insulin is produced by the pancreas.
Action of insulin
| Low glucose | High glucose | |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin level | low | high |
| Effect on liver | Does not convert glucose into glycogen | Converts glucose into glycogen |
| Effect on blood glucose level | increases | decreases |
Insulin in the presence of high glucose causes the liver to convert glucose into a molecule called glycogen, which is used for storage
When there is no insulin, and there are low levels of glucose in the blood, molecule called glycogen is converted into glucose.
When insulin does not work properly this can cause diabetes. Diabetes is a condition where the blood glucose level remains high.. there are two types of diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is when there is ac complete lack of insulin. The insulin is not produced in the body, this is usually due to a genetic defect from birth
Type 2 diabetes is when there is plenty of insulin but it is not working properly, as the person has become resistant to it.
The menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a cycle of approximately 28 days. It is process in which the uterus lining builds up in anticipation of the arrival of an egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the uterus is shed and released in blood through the vagina.
Hormones play a key part within the menstrual cycle.
FSH – it is produced in the pituitary gland and it causes the egg to mature and causes the ovaries to release oestrogen
Oestrogen – it stops FSH from being releases and causes the uterus lining to thicken. Also stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH
LH – causes the egg to be releases on day 14
Progesterone – it helps to maintain the lining of the uterus for the rest of the menstrual cycle, if fertilization occurs then progesterone levels remain high, if not then the progesterone levels fall and the uterus lining breaks down.
Control in plants
Plants are sensitive to light, moisture and gravity. Therefore when a plant grows it will try to grow towards the light, and towards water. Sometimes gravity can help the plant achieve this.
Plants growing with the light are known as phototropism, whereas a plant growing with gravity is called geotropism.
Different part of the plant will respond to different things. The stem will respond to light but will not respond to gravity. Therefore this is knows as positive phototropism and negative geotropism
The root of the plant is the opposite to the stem. It responds to gravity but does not respond to light, as it is underground. Therefore it is knows as a positive geotropism and negative geotropism
Auxins
Auxins are a group of hormones that are only present in plants. They are mostly present in the tips of the stems and roots. The auxins help certain grow more and faster.
The auxins present in the stems help it grow faster, the auxins present in the roots causes a decrease in growth rate.
If a plant was growing the side that is not facing the sun will have more auxin and therefore grow more causing it to bend towards the sun. this is highlighted in the picture
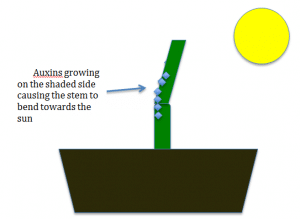
In roots the auxins causes less growth upwards and causes it to bend down in the direction of gravity therefore the roots can get further into the ground.
Nerves and Hormones
L.O To learn about the nervous system and how it works and how hormones can control conditions inside humans and plants.
To learn about the nervous system and how it works and how hormones can control conditions inside humans and plants.
Nervous system
The human nervous system consists of two parts:

The central nervous system is the main control centers like the brain and the spinal chord
The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves, which reach the rest of the body which is also known as the periphery
Nerve cell
Nerve cells can also be called neurons and carry messages known as impulses

Nerves carry the impulse through the body and then the nerve is sent to the rest of the body through the dendrites which have many other nerves attached to it.
There are two types of neurons sensory and motor neurons
Sensory neurons are involved in relaying the impulses from the point of impact or otherwise known as the receptors to the central nervous system
The central nervous system then decides what action to take, and it then send another set of impulses through a set of motor neurons to the effector.

Receptors
Receptors are a group of cells, which help to detect a change in the environment for example, your skin will detect if the temperature change around you.
Your skin can also detect pain and it will be send an impulse to the CNS which will then respond to move you body part away from pain.
Your eyes will respond to the light by either dilating or constricting
Effectors
Effectors are parts of the body that respond to what the receptor has felt. This can come in the form of a muscle contracting or a gland releasing a hormone or saliva.
The effector will then stimulate a response.

Reflex actions
A reflex action is the way the body quickly reacts to dangerous situations. It follows a sequence which does not involve the brain

This nerve action is called the reflex arc
The reflex arc process –
- The receptor detects the stimulus
- Sensory neurons send the impulse to the spinal chord
- The spinal chord sends an impulse via the motor neurone
- The effector then responds
The synapse
Where two neurons join together, there is usually a tiny gap called a synapse. the impulse crosses this gap in the for of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These diffuse across the gap and continue the synapse

Hormones
The conditions in our body are carefully controlled by hormones, to ensure that everything is constant and our body functions efficiently.
There are several aspects of our body that need to be controlled. Body temperature needs to be controlled to ensure that the enzymes can work efficiently
Blood sugar levels need to be controlled to ensure the brain has the correct levels of glucose
Water content also needs to controlled to ensure our cells have the correct amount of water. Too much water can cause cells to burst and too little will cause cells to shrink.
Hormones use a system called negative feedback, which allows them to maintain the conditions at just the right level.

One of the main hormones in the body is insulin. Glucose levels are regulated in the body by insulin which ensures that the levels do not get too high or too low. Insulin is produced by the pancreas.
Action of insulin
| Low glucose | High glucose | |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin level | low | high |
| Effect on liver | Does not convert glucose into glycogen | Converts glucose into glycogen |
| Effect on blood glucose level | increases | decreases |
Insulin in the presence of high glucose causes the liver to convert glucose into a molecule called glycogen, which is used for storage
When there is no insulin, and there are low levels of glucose in the blood, molecule called glycogen is converted into glucose.
When insulin does not work properly this can cause diabetes. Diabetes is a condition where the blood glucose level remains high.. there are two types of diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is when there is ac complete lack of insulin. The insulin is not produced in the body, this is usually due to a genetic defect from birth
Type 2 diabetes is when there is plenty of insulin but it is not working properly, as the person has become resistant to it.
The menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a cycle of approximately 28 days. It is process in which the uterus lining builds up in anticipation of the arrival of an egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the uterus is shed and released in blood through the vagina.
Hormones play a key part within the menstrual cycle.
FSH – it is produced in the pituitary gland and it causes the egg to mature and causes the ovaries to release oestrogen
Oestrogen – it stops FSH from being releases and causes the uterus lining to thicken. Also stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH
LH – causes the egg to be releases on day 14
Progesterone – it helps to maintain the lining of the uterus for the rest of the menstrual cycle, if fertilization occurs then progesterone levels remain high, if not then the progesterone levels fall and the uterus lining breaks down
Control in plants
Plants are sensitive to light, moisture and gravity. Therefore when a plant grows it will try to grow towards the light, and towards water. Sometimes gravity can help the plant achieve this.
Plants growing with the light are known as phototropism, whereas a plant growing with gravity is called geotropism.
Different part of the plant will respond to different things. The stem will respond to light but will not respond to gravity. Therefore this is knows as positive phototropism and negative geotropism
The root of the plant is the opposite to the stem. It responds to gravity but does not respond to light, as it is underground. Therefore it is knows as a positive geotropism and negative geotropism
Auxins
Auxins are a group of hormones that are only present in plants. They are mostly present in the tips of the stems and roots. The auxins help certain grow more and faster.
The auxins present in the stems help it grow faster, the auxins present in the roots causes a decrease in growth rate.
If a plant was growing the side that is not facing the sun will have more auxin and therefore grow more causing it to bend towards the sun. this is highlighted in the picture

In roots the auxins causes less growth upwards and causes it to bend down in the direction of gravity therefore the roots can get further into the ground.


