Photosynthesis
L.O To learn how photosynthesis and learn what affects the rate of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process required by plants to produce energy. The process involves absorbing the sunlight and making energy. Photosynthesis is a very important process in maintaining the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide + water à glucose + oxygen
Photosynthesis takes place in plants cells in small subunits called chloroplasts which contain a small green pigment called chlorophyll These green pigments help to absorb light and convert light into energy which can be used by the plant.
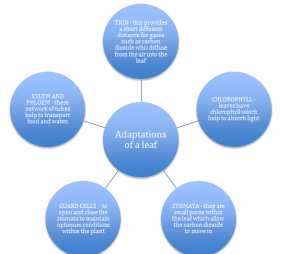
Adaptations of a leaf
Leaves are made of different components
- The leaf has a mesophyll layer where most of the photosynthesis occurs
- It has xylem and phloem which help to transport the substances around the plant
- It also contains epidermal tissue which covers the whole leaf
Taking these graphs into account, you can artificially control the environments for plants. This can be done in a number of ways:
- A greenhouse can be used to trap the suns heat in order to make sure that the temperature is no longer the limiting factor
- To make sure light is not the limiting factor, artificial lights can used to ensure photosynthesis occurs
- Carbon dioxide can also be an issue, however this can be slved using a paraffin heater which provides carbon dioxide
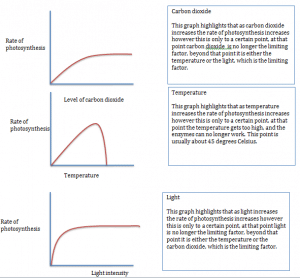
Light
A leaf has many parts. The top of the leaf is known as the waxy cuticle, which protects the leaf and prevents water loss.
The upper part of the leaf is where the sunlight hits. Therefore the upper part of the leaf has many palisade cells (for photosynthesis). These palisade cells have many chloroplasts and look like the plant cell drawn above.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide enters the plant through small pores in the leaves called stomata. Guard cells control these pores and help maintain the conditions within the plant and help it adapt to the conditions outside for example weather.
The lower part of the leaf cell is called the spongy layer. It has many gaps, which allows the carbon dioxide to move around and reach other cells.
Water
Water is absorbed from the ground. The roots have root hair cells, which are adapted to getting the maximum amount of water from the ground. There are long and thin , which allows them to reach the maximum area, also they have very thin walls thus reducing the diffusion distance for water.
The rate of photosynthesis
The rate that photosynthesis occurs is dependent on a variety of conditions. By looking at the equation you would guess that a plant would need a large amount of water and carbon dioxide for the highest rate of photosynthesis to occur.
There are also other variables to take into account such as temperature and sunlight. If any of these are lacking then it is called a limiting factor
The limiting factor also depends on the environmental conditions:
- At night the obvious limiting factor is sunlight
- In the winter months it is temperature
- And in the summer months, when it is warm and bright, carbon dioxide can be the limiting factor
Rate limiting graphs
Taking these graphs into account, you can artificially control the environments for plants. This can be done in a number of ways:
- A greenhouse can be used to trap the suns heat in order to make sure that the temperature is no longer the limiting factor
- To make sure light is not the limiting factor, artificial lights can used to ensure photosynthesis occurs
- Carbon dioxide can also be an issue, however this can be slved using a paraffin heater which provides carbon dioxide
How do plants use the glucose
Once photosynthesis is complete plants use glucose in a number of ways
- Respiration – it is used in respiration to produce energy
- Cell walls – glucose can also be used in making cell walls in a plant, especially one that has a fast growth rate
- Protein – glucose can be turned into protein.
- Seeds – glucose can be turned into fatty substances called lipids which are then stored in seeds
- Starch – the glucose if not used can be stored as starch, and can be used when
the rate of photosynthesis is low. Starch is insoluble which makes it better for storage


