Cells
L.O To understand the difference between plant and animal cells and to learn about the different cells and there functions.
All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells are the building blocks of life. Because there are a vast number of cells, some cells are specialized to ensure they provide a specific function.
Specialized cells
|
Type of Cell |
Function |
Special Features |
|
Red Blood cell |
To carry oxygen in the blood. |
Has hemoglobin which carries the oxygen Has a concave, donut like shape Does not have a nucleus so it can carry more oxygen Has a large surface area to allow to carry more oxygen |
|
Nerve Cell |
Carries nerve impulses (messages) from the body to the brain and back again. | They are long, have many connections so can reach every corner of the body
They carry electrical signals so the impulse is relayed quickly |
|
Egg cell |
To join with the sperm cell and provide nutrition for the zygote (new cell) when formed. | It is large and contains lots of cytoplasm for reaction to take place. |
|
Sperm Cell |
To reach the egg cell and join. | Has a tail, which allows it to move.
Also has a head to carry genetic information and penetrate the egg cell. |
|
Root Hair Cell |
To absorb water and minerals. | Has a large surface area, which allows it to absorb as much as possible. |
| Palisade cell (Leaf cell) | To absorb sunlight to allow the plant to photosynthesize. |
Has a large surface area and many chloroplasts, which allow it to absorb as much sunlight as possible. |
EXAM TIP
Never call the nucleus the “brain of the cell”, it is not a very good description and will not get you any marks.
EXAM TIP
Learn the difference between animal and plant cells, as it is a very common question.
Animal cells and plant cells
Animal cells have a very irregular shape and often look uneven and unequal however plant cells have a very regular shape. Plant cells and animal cells differ in function due to the different parts they have.
This is highlighted in the diagram below
|
PART |
FUNCTION | FOUND IN |
|
Cell membrane |
Outer part of cell, which acts as a barrier controlling what goes in and out |
Animal and plant cells |
|
Cytoplasm |
This is where all the reactions occur |
Animal and plant cells |
|
Nucleus |
Controls the cell and carries all the genetic information |
Animal and plant cells |
|
Chloroplast |
This is where photosynthesis occurs as it contains chloroplasts |
Plant cells |
|
Vacuole |
Keeps the cell firm as it contains a liquid call cell sap |
Plant cells |
| Cell wall | Outer wall which supports the cell ensuring its structure |
Plant cells |
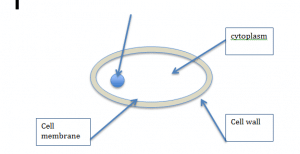
Unicellular organisms
A unicellular organism is one that only has one cell for example bacteria, protozoa and fungi.
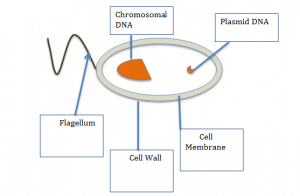
Bacteria
Bacteria are very small cells, they differ from normal animal cells as they do not contain a nucleus so the DNA is either floating free or kept in small containers called plasmids they also may have a tail like structure usually called a Flagellum allowing the cell to move.
Protozoa
Protozoa are also unicellular organisms however it has certain characteristics that are similar to animal cells. It has feet like projections that allow it to move and take food into the cell.
Yeast
Yeast is commonly used in bread making and making alcohol as it converts sugar into alcohol. Yeast is similar to plant cells in that, they have cells walls, which means they can absorb sugars.
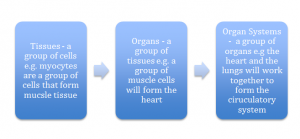
Cells, tissues, organs and systems
Tissues are a group of cells working together to perform a specific function e.g. muscle, lining the intestines or lungs .
Organs are a group of tissues which work together to perform a larger task e.g. heart, lungs, stomach.
Organ systems are a group of organs working together to perform a task in the body e.g. Cardiovascular system or the reproductive system.
Diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of particles from one place to another. Diffusion usually occurs in both gases and liquids, as those particles are free to move around. A common type of diffusion occurs in gases, as one set of gas particles will move from one area to another. The gas particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
This explained in the diagram below.

Cell membranes help with the diffusion process. Cell membranes not only help keep the structure of the cells, but also control what moves in and out. The cell membranes have tiny holes, which allow small particles such as oxygen to pass through, but they do not large particles such as protein to pass through. That is why proteins have to be broken down into smaller articles such as amino acids


